Surrounding
This gravitational model is called "surrounding", "Surrounding Matter Theory" (S.M.T.), or "Surrounding Gravitational Model". It applies only at astrophysics scale. It is a direct prediction of "relativity". But it can be understood independently of it in a standalone manner, like any Newton's law direct modification.
The idea at the construction of this model is that the energy in the surroundings of the location where the force is exerted plays also a role in the equations of gravitation. GR tells us that the mass of an attracting object is determinating the modified space-time around it and therefore, gravitational acceleration. But in this new model, when calculating this gravitational acceleration in some given space-time event, one must also take into account the matter density in the surroundings of this location.
This modification of GR generates a behavior in which space-time happens to have an "elasticity". And the elasticity modulus is roughly proportional to matter density at the location where the gravitational force is calculated.
The one and only article about surrounding was published in 2018 in EPJ and also in the proceedings of the CSS2018 conference (pages 204 to 228). You can download the latter here too: Surrounding.pdf
Here are the programs which I used in this paper for illustrating the model's behavior:
Galaxy simulation: stet.7z
Bullet cluster: simubull.zip
Here is one result of the galaxy simulation:
Newton's law structure of a simulated galaxy
This N-body simulation shows, as usual, Newton's law being ruled out by experimental data. Even the elliptical galaxies do not comply with this "ball" matter distribution : https://youtu.be/VwNobSUsOdw
Same simulation replacing Newton's law by surrounding
This one shows a fast rotating bar with its unrolled arms as well as a ring galaxy and generated dwarf galaxies. Could you dream more than that ? MOND shows also bars and well unrolled arms in its simulations. Indeed, this is the signature of a well working modified gravity, because it means, notably, that the gravitational force is strongly reduced far from the galactic center. But the ring galaxies are only predicted by surrounding, as far as I know. Those simulations show also that surrounding is a real engine for creating dwarf galaxies, and this is also a very good prediction. Please refer to the "ring galaxies" and "dwarf galaxies" paragraphs below.
Newton's law speed profile of a simulated galaxy
The famous speed profile of our usual Kepler law, completely ruled out by experimental data : https://youtu.be/HvSypM3iXLQ
Same simulation replacing Newton's law by surrounding
Here not only the overall profile is retrieved, but also the dynamic is much increased, comparing with Newton's law. This is confirmed also by the calculations. Notably, those calculations predict the existence of negative gravitational force. Those two features are quite specific features of surrounding. For example, negative forces are inexistent in MOND, and the resulting dynamic is weaker.
Comparison of MOND and surrounding
By the way, a specific paragraph must be written about the comparison of MOND and surrounding. No mention about any other modified gravity, simply because MOND is the best. Those two models share the same predictions in, may be, more than 90% of the astrophysical and cosmological cases. Indeed, MOND increases Newton's law gravitational force when acceleration is low, and surrounding increases it when surrounding matter density is weak. But when acceleration is low, most of the times, it means that surrounding matter density is weak. My personal tendency in this blog is to focus on the remaining 10%, that is, on the cases in which MOND and surrounding predictions are different. This is because that's were things are interesting. But MOND is still valid today after 40 years, and was the only real modified gravity, abble to show so many times how much dark things were wrong solutions. Now it is well established that dark things do not exist. And MOND has helped us to support this strong scientific improvement of rulling out dark things definitively. A big work remain to do in the study of the several cases when the predictions of MOND and surrounding are different. Based on today's review, surrounding shows better predictions than MOND in those cases. Surrounding appears very much as an improved version of MOND. Of course there are several different versions of MOND, as well as there can exist several different versions of surrounding. Indeed, there are some degrees of liberty of the models.
Here are the slides presenting the surrounding model: Surrounding.pdf Surrounding.pptx
Particularly interesting topics
Ring galaxies
For me this is the most fantastic result of surrounding. Ring galaxies are generated easily in the simulations. But the ring galaxies are only predicted by surrounding, as far as I know. I tried to find a correct explanation of those ring galaxies in the literature by another modified gravity, or by actual relativity. By I did not succeeded. Please tell me!
Dwarf galaxies
The dwarf galaxies are extremely testing in the surrounding model because the model simulations I have done of a galaxy, not only retrieve the correct structure with well enrolled arms and bars (like does MOND) but also it generates ring galaxies and a high number of dwarf satellite galaxies. Those 2D simulations show that surrounding behaves like a big engine for creating dwarf galaxies. That's why 3D simulations are very much required.
Notably, the Vast Polar Structure (VPOS) mystery is interesting. As it is often the case, the MOND explanation of it is probably shared by surrounding. This is because those two models are similar for their main modification of Newton's law. But here surrounding suggests another possible explanation, which is based on its very particular feature, the potential well of the 15 kpc ray surrounding sphere. I summarize this in a small notice.
Galaxy stability
This is also a topic in which the particular surrounding potential well is interesting. Surrounding predicts the following, in any configuration in which matter density is weak or very weak.
For any bunch of matter, the stability is greater than what is predicted by Newton' law. And the weaker is the surrounding matter, the more the bunch of matter is stable. Therefore this is particularly true for a dwarf galaxy, which is a small bunch of matter. This is extremely valid in the case of an ultra-faint dwarf galaxy (UFD). Indeed, for those UFDs, the surrounding matter density is probably extremely weak (IGM matter density is probably weak). Once again this is confirmed by experimental data. And this UFD stability is an issue for MOND.
Spiral galaxies with fast rotating bars are also much more stable in surrounding than with MOND. This stability is an issue with MOND. For surrounding, no such issue since the fast rotating bar is simply the nucleus of the ring galaxy: nothing more stable than that.
LSB and UDG
Low Surface Brightness (LSB) galaxies and Ultra Diffuse galaxies (UDG), are extremely interesting. That's because the simulations show that, at the very end of a given simulation, if the IGM is low enough, then a corpse of the galaxy remain allways, which is elliptical, and very faint.
More generally those simulations show that a surrounding prediction is the following. Each galaxy type (ring, bar, spiral, elliptical, LSB) behaves like an age in the life of any galaxy (that is, but not respectively, young, mature, old, very old, dead).
Is this "aging feature" something already known from observations ? I dont know yet, humbly. I tried to find this prediction in the literature, but I could not. Therefore this might be a new kind of prediction. This might not be something either observed or directly proven to be true from observations. Please tell me.
Bullet cluster internal dynamic
In the following excerpt from my article you must replace "SMT" by "surrounding", it was the old name (Surrounding Matter Theory). "rmax" is equal to 15 kpc.
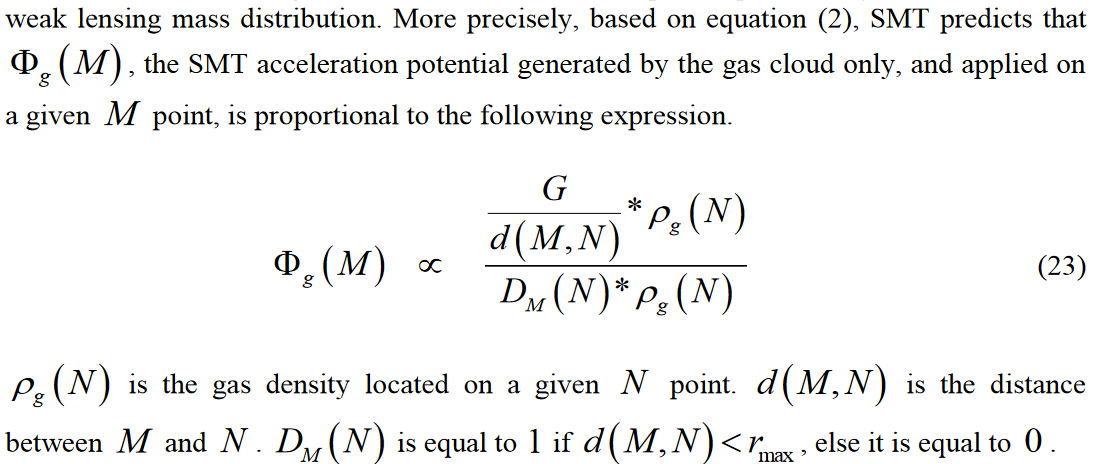
So you see the explanation here is extremely simple. The attraction potential coming from the gas alone is roughly dissolved by the surrounding potential. The numerator is Newton's law convolution. And it is almost completely tamed by the surrounding convolution of the denominator. I wrote "almost", because even though the G/d(M,N) and Dm functions are very similar, they are not exactly the same.
And I even pretend that those slight differences generate effects which are noticeable in the weaklensing result of the bullet cluster. That is to say, on some images which are the results of the weak lensing, it appears for example shapes like a ![]() . I pretend that this
. I pretend that this ![]() at these exact locations where the gas begins to dissolve is probably exactly what is predicted by surrounding. I wrote "probably" because I did not make any completely rigourous demonstration. But this is obvious because the disapearance of the gas in the convolution of the denominator, like with a pole in a denominator, generates a "jolt".
at these exact locations where the gas begins to dissolve is probably exactly what is predicted by surrounding. I wrote "probably" because I did not make any completely rigourous demonstration. But this is obvious because the disapearance of the gas in the convolution of the denominator, like with a pole in a denominator, generates a "jolt".
Bullet cluster speed
The speed of this cluster of 4700 km/s is a big issue, too. But such a velocity at this red-shift should come as no surprise with surrounding. Indeed, in the voids, which exist at this red-shift with surrounding, G is increased by a multiplicative factor of 40. This huge acceleration explains such a speed. It should be very interesting to simulate and refine this mechanism.
In 2023, the existence of El Gordo cluster was revealed with James Webb Space Telescope. The measured velocity was about 2500 km/sec, but also its mass and red-shift are impossible to explain with today's cosmology.
Large scale structures
Jean's lengh is today 5 times greater than what predicts Newton's law. Moreover collapse calculation is no longer driven by Universe’s expansion, like Newton’s law collapses are. Also, the predicted age of the universe is 100 Gyr. All this allows for the creation of voids and walls structures.
An exact equation is given by the model for the shape of the walls and voids structure. The result is closed to experimental data (to say the least, it is much closer than Newton's law prediction).
But here the prediction is not only that these large scale structures are predicted. It is that the predicted structure is a stable equilibrium. Once again, can we dream more than that ?
Cosmology
The prediction is simply a de Sitter universe. But cosmological constant is not required because matter density is replaced by a constant which is critical matter density. This replacement is the direct prediction of surrounding fundamental mechanism. Acceleration of expansion is predicted with a q parameter equal to -1, space curvature is equal to 0.
From this, all the problems of today's cosmology are solved at once : critical universe density, fine tuning, singularity, particle’s horizon, acceleration of Universe’s expansion, space curvature, cosmological constant, age of the universe. Nucleosynthesis is not predicted correctly but this should come as no surprise since surrounding does not apply to the radiative era.
In 2023, with James Webb Space Telescope, the age of the universe becomes a huge problem. This has been for long a big problem. For example, in 1993 we knew that the well formed NGC 2885 galaxy was not possible, and in 2013 we knew that UDFj-39546284 galaxy existence is impossible to explain with a 13 Gyr old universe. But in 2023, with James Webb Space Telescope, the age of the universe becomes an even bigger problem. Now galaxies are seen, which age are only 400 Myr after the big bang. Surrounding predicts an age of the universe of 100 Gyr (time since last scattering). With such an age such objects can exist.
Next to come
I still have to write another article, about those "next to come" topics below.
Tully-Ficher law
Surrounding is compatible with Tully-Ficher relation. I have executed dedicated simulations for it. It will be required for that a slight modification of surrounding, which is that the 15 kpc limit will decrease slowly, inside of any galaxy, with the galaxy radius. A good news is that, associated with that compliance with Tully-Ficher law, the galaxy speed profiles are improved.
Train wreck cluster
This is a new astonishing astrophysics discovery. Surrounding might give a clue here because it predicts that the gravitational weak lensing of a vacuum is weaker than what is expected with Newton's law. If a vacuum density is equal to x, then the generated gravitational lensing is not proportional to x but to x/(x+xu), where xu is universe matter density at vacuum time. The result is a weakening of the gravitational effects of IGM heterogenetities. This is not be confused with the explanations of why there are so many heterogeneities (for that please refer to "Large scale structure" paragraph, above).
To be developed.
Correlation of the surrounding ray with ring galaxies, bar lengths, and speed profiles
Surrounding predicts such a correlation. This correlation is shown by the N-body "toy" simulations. It is still very important to execute simulations which are as simple as possible, in order to understand correctly their final result. Any added mechanism (such as the decrease of the star velocities by gas for example) would make it difficult to discriminate what is the result of what at the end. The use of a simulation is not something absolute but relative. You have to execute the same, simple, simulation, on different models. And then you can conclude something by comparing their results.
This correlation is the result of the potential well created by the surrounding effect. The size of this well predicts all at once several measurable values, like ring galaxy rays, bar lengths of bar galaxies, lengths of speed profile flat parts. In fact the latter value is more "diffuse", it's more the evolution of the shape of the speed profile with galaxy mass.
In the today's version of surrounding, the ray of the surrounding sphere is constant equal to 15 kpc. In the next version this will be varying, as explained above for the Tully-Ficher law. The correlation study will allow to tune this varying function.
Here the study consists of recollecting the relevant experimental data and execute statistics on them in order to rule out or to confirm the correlation. I need some help from skilled people there!
Below are some interesting questions, received during the conferences after my talks, or by mail
Why would nature change its law after 15 kpc ?
I don't know. May be there exists some shielding effect during the propagation of the gravitational interaction, provoked by such things as dust or gas. We already know that shielding effects exist for the other forces. Many models or theories just do not explain much why they pretend to change the "laws of nature". Often modifying gravity theories does so without explanation, as far as Newton's law is a "law of nature".
Why and how the alpha parameter is modified when one goes from the inside to the outside of a galaxy ?
The same shielding effect might exist, please refer to the above answer. It would explain why there is a much lower value of this parameter inside of a galaxy, than outside of it. That's about the "why". About the "how", of course it would have beed easy to state that the value of this parameter changes slowly between its 2 main values. It has been so with the famous "a0" parameter of the MOND model, for example. This was quite mandatory for MOND because the "a0" parameter is in the inner part of this model, and its specification must be done completely. At the contrary, here with surrounding this parameter is not so much fundamental. And the comparisons which are done today, of surrounding, with experimental datas, do not need such a detailed specification of "alpha". Another argument is that it requires a whole paragraph to detail such a detailed specification. And the lenghs of articles are often very much constrained.
What meaning one can give to an infinite potential ?
(This question relates to the equation (23) of my article, in which a null value can theoretically be used). In fact the equation (23) I was reminding is only an approximation of the surrounding equation. Please refer to my article. You are right, this approximation yields serious issues when used outside of its validity context!
Looking forward for collaboration
I am looking forward to any kind of collaboration. Any collaboration proposal is very much welcome. In particular I need help for the execution of 3D simulations of galaxies and clusters. Notably the Vast Polar Structure mystery, and every mystery related to galaxy stability such as the ultra-faint galaxy mystery, might be interesting to adress with 3D simulations. Also the big mystery of the ring galaxies might be very interesting to simulate in 3D.
August 2023.
